Autonomous Transport Advances Rely on AI, Ecosystem Progress
Autonomous Transport is an important area for AI, as it plays a large part in not only controlling vehicles, but also providing real-time decision-making.
November 20, 2018

By Michael Azoff
An important application for artificial intelligence (AI) is autonomous transport. All areas of transport are being investigated for autonomous control, with AI playing a large part in driving/piloting control and providing intelligent decision-making in real time based on data from an array of sensors. These include light spectrum (cameras), radio (radar), laser (lidar), positioning (global navigation satellite system, GNSS, such as GPS), inertia using inertial measurement unit, and IOT (vehicle-to-everything) communications. Ovum is seeing progress in autonomous vehicles, trucks, aviation, trains, and nautical vessels.
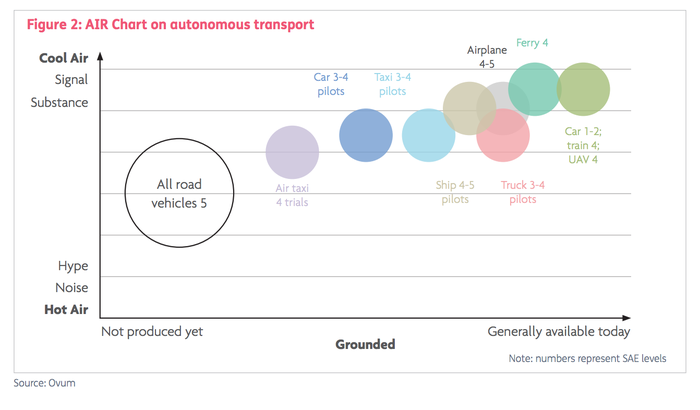
The December 2017 Ovum AI Reality (AIR) chart provides a qualitative view of progress in autonomous transport. 2017 saw many milestones achieved as ventures from start-ups, technology companies, and transport industry incumbents staked their position in trials and pilots. The scope of the topic is potentially huge, including regulations, legal issues, security, safety, geographical differences, smart cities and more, but this report is strictly concerned with the advance of AI in autonomous technology. The AIR chart is based on current state-of-the-art progress. In addition, we offer a view on when autonomous vehicles will become a common sight on our roads.
Autonomous Transport is Driving Toward Reality
Progress in autonomous transport is already seeing road, rail and air examples
The impact of autonomous transport on society will be huge, and will affect urban architecture, road building and parking spaces, patterns of transport use, driving/piloting skills and de-skilling, and more. In light of the role of cars in our culture, there will be a deep impact on how we live. Technology is incrementally pushing forward and the motivation exists, with recognition all round that this technology will save many lives (in the U.S. there is a traffic accident fatality every 15 minutes). There will also be job changes, and while demand for drivers/pilots will undoubtedly decrease, new jobs will be created to design, build, maintain and monitor autonomous systems.
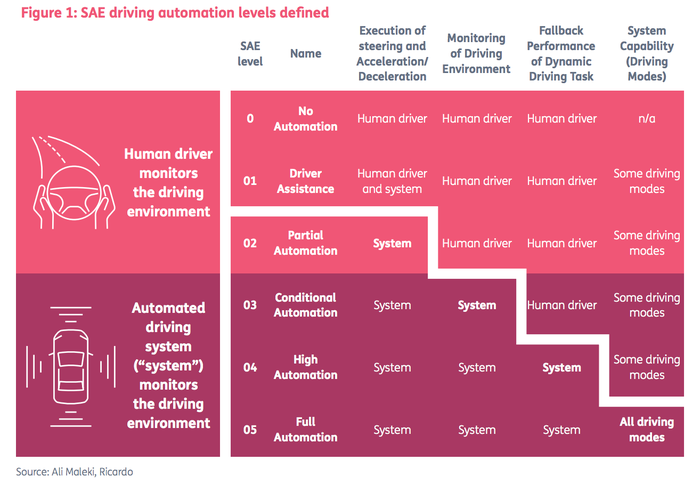
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) International defines five levels of autonomous driving (see Figure 1). In our analysis, we stretch the use of SAE levels to generic modes of transport with similar autonomous system capabilities at the corresponding levels. One provision should be noted in extending SAE this way. While mass-market vehicles will be truly autonomous with no centralized control, we expect commercial operations, at least in the first wave of this technology, to have a degree of remote monitoring, with the capability for humans to take over if necessary. This is not reflected in the SAE level
Major road transport manufacturers (Tesla, for example) envisage level 4 capability in a few years, or over 10 years, and are striving to achieve this goal. Creating an autonomous driving industry has become a nation state race. For example, the Obama administration kick-started billion dollar investments in the U.S., and in recent weeks the UK government pledged investment and relaxed regulations to encourage research in the UK, following on from its UK Autodrive initiative, which is currently running autonomous driving trials in Milton Keynes and Coventry.
In the assessment below, we refer to “level 3-4 pilots”, which should be interpreted as a system being developed for level 4, but having a test driver on board who can take over makes it in effect a level 3 system during testing. Some of the milestones in autonomous transport that helped define the December 2017 AIR chart are as follows.
Air taxi and drone: Volocopter demonstrated an eight-minute level 5 autonomous flight without passengers on Sept. 25, 2017 in Dubai, UAE. Amazon Prime Air is trialing a pilotless drone delivery service, with the first delivery to a real customer accomplished in December 2016 in Cambridge, UK. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are already common in the military.
Airplane: Aircraft are already highly automated, and fully autonomous flying is likely in the next decade. For airlines, passenger sentiment not the technology may be the main barrier. Unlike air taxis, where airplanes fly and take off and land is highly controlled.
Car: Waymo (owned by Google owner Alphabet) has been trialing level 4 autonomous vehicles in Phoenix, Arizona without drivers on board since November 7, 2017. The level of activity was kick-started by Google and Tesla, but established motor manufacturers are very much in the race, including BMW, Daimler, Ford, Honda, GM, Nissan, and Toyota, as well as start-ups.
Ship: Level 5 autonomous ships and ferries are being developed, including by Rolls Royce, which predicts the first examples to be short-distance ships such as car ferries, and ocean-going robot cargo ships in 10 to 15 years. Norway’s Yara and Kongsberg are jointly working on building the first crewless ship, the Yara Birkeland, for cargo shipping in Norwegian waters. Autonomy will be added in stages with level 4-5 expected to be achieved by 2020.
Submarines: There is a history of autonomous underwater vehicles but there is activity in creation of a new generation. Boeing and the U.S. Navy are, for example, working on autonomous submarine drones.
Taxi, bus, shared-ride services: The first level 4 autonomous taxis were trialed in Singapore by nuTonomy in 2016. Navya offers Autonom Cab, a robot taxi designed for level 4 autonomous driving with no cockpit, steering wheel, or other manual controls. A Navya bus has been in operation in Lyon, France, since 2016. Tesla has delivered 50 vehicles to city of Dubai, UAE, for an autonomous taxi service. Waymo plans to open its autonomous taxis to passengers in Phoenix in early 2018. Zoox is planning to have customers by 2020. Uber and others are researching driverless taxis. An autonomous bus system is being trialed in Las Vegas. In December 2017, Lyft, in partnership with nuTonomy, is matching passengers in select areas of Boston with autonomous rides. The UK Transport Research Laboratory’s Harry shuttle has been trialed with the public in Greenwich, London.
Train: Driverless train systems have been in operation since 1967, either with a driver monitoring the automated system, or driverless but with staff on board. The first freight train using an autonomous system without a human on board ran on Oct. 2, 2017 and was operated by Rio Tinto in its iron ore network in Western Australia and monitored from an operations center in Perth.
Trucks: Rio Tinto has been operating level 4 autonomous trucks in its iron ore mining in Western Australia for some years. Embark and other truck operators have been piloting level 3-4 autonomous trucks on public interstate highways in the USA in 2017, with drivers taking full control over the first and last miles.
December 2017 AIR Chart on Autonomous Transport
The December 2017 AIR chart is shown in Figure 2. It is notable that road transport level 5 is still some years (perhaps a decade) away from being realized. This, however, does not take account of further improvements in the core technology, particularly AI, which is improving incrementally. Algorithms are being refined (for example, deep level architectures), computing power is increasing annually, and new AI hardware accelerators expected to reach the market in 2018 will add to this rate of improvement. These improvements in the technology will bring SAE level 4 and ultimately level 5 autonomous driving to fruition earlier than expected.
Some modes of transport are ahead of road transport. Aircraft, due to the highly regulated control of their paths, are at levels 4 and 5. Similarly, nautical vessels have less complexity in their environment and are at advanced levels.
The sheer size of the car industry makes it a particularly important area of focus. Many contenders will bring level 4 and eventually level 5 vehicles to our roads. In the U.S., there are more than 25 companies currently registered in California to trial autonomous cars. Other states attracting research include Arizona and Pennsylvania.
A metric of proficiency used by the Department of Motor Vehicles in the state of California is the number of autonomous miles achieved per disengagement. The most recent figures released relate to 2016. Ahead of the pack is Waymo (owned by Alphabet) at 5,128, followed by BMW at 638, Nissan at 246.7, and Ford at 196.7. Waymo has received the most funding of the contenders, at more than $1 billion, and has been longest established (2009), accruing the most miles of actual road testing (3.5 million) and simulation (3 billion).
Autonomous Driving Technology Is Powering Next Generation Vehicles
Because of the array of sensors needed, building autonomous vehicles is not cheap. All manufacturers use a range of different sensors, including lidar. The exception is Tesla that so far relies solely on cameras and radar. The cost of the sensors per vehicle suggests the most economical model would be for autonomous technology to be used for shared-ride and taxi services, with expensive models available in the top end of the private car market. However, the cost of the sensors continues to fall. Cruise (the GM acquisition made in 2016 to establish itself in the race), acquired lidar manufacturer Strobe in October 2017 and expects a 100 percent reduction in lidar costs.
A key provider of technology for AI-based autonomous transport is Nvidia, whose GPUs are an essential ingredient for training and inferencing AI systems. Nvidia Drive PX is an AI car computer appliance, housing Nvidia’s high-end GPUs and other advanced microprocessors and sensors, and built to support ASIL-D, the highest level of automotive functional safety. Nvidia says it has partnerships with most of the leading car manufacturers in the race to bring autonomous vehicles to the roads. Another provider of GPUs into this market is AMD. Intel announced in 2017 a partnership with AMD to deliver a joint CPU and GPU solution, and acquired Mobileye, a start-up developing autonomous driving technology. Baidu is making its Apollo autonomous driving platform part open source, and its partners include Daimler, Ford and Nvidia.
New AI hardware accelerators are expected to reach the market in 2018 and it remains to be seen if they can outperform the best GPUs, and raise the computing capability to run ever larger AI architectures that yield higher performance and accuracy. Even if these novel AI accelerators disappoint, the year-on-year improvements in GPU performance are expected to continue. We therefore see a continuing upward trend in AI system performance over the next decade.
Autonomous transport will comprise of connected machines and will therefore be part of the Internet of Things (IoT). Much IoT technology will therefore also be relevant to autonomous transport, as will smart cities, 5G, and telemetry, which will also play an important role in future autonomous transport, and create opportunities for IoT and telco vendors. Ovum expects autonomous driving capability at SAE level 4 to appear in the next few years in trucks and passenger services such as shared rides, taxis, and buses. Examples already exist. Cars at level 4 will not be good enough for people that, for example, need to rely on their car and not being able to use it when it snows is not satisfactory.
An autonomous car at level 5 is yet further away because the AI technology needs to improve. However, the current incremental pace of AI evolution means it is not a question of if but when. In the near future there will be an identical overlap between an Uber/Lyft style service, a taxi ride, and a car rental that comes with a (virtual) robot chauffeur and arrives at your door. Such car usage will reduce the number of cars needed in society, and the impact of this scenario on the car industry will be far-reaching.
Principal Analyst Michael Azoff is a member of Ovum’s IT infrastructure solutions group, leading a range of software development and lifecycle management research initiatives.
For more information about IoT research and analysis from Ovum, which belongs to the same corporate family as IoT World Today, send email to [email protected].
You May Also Like



.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)

.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)